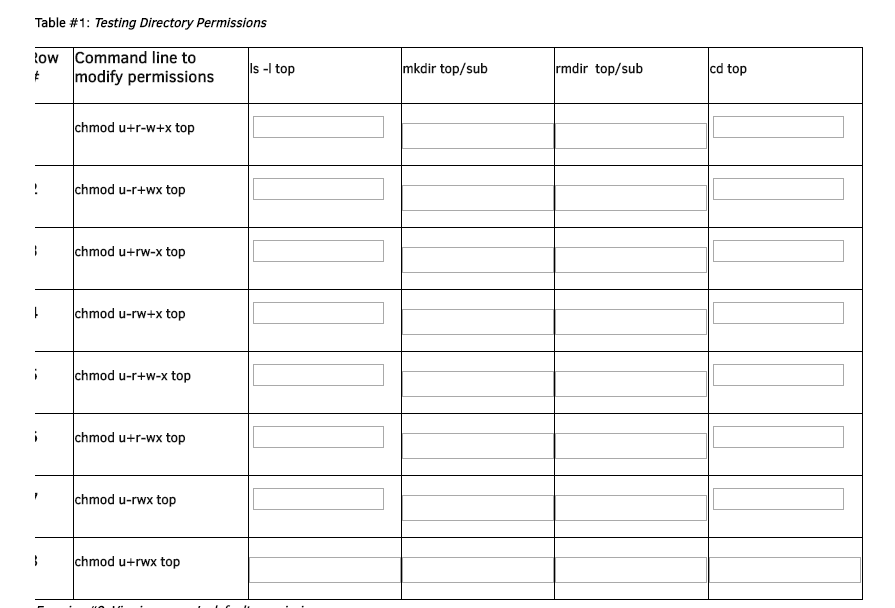
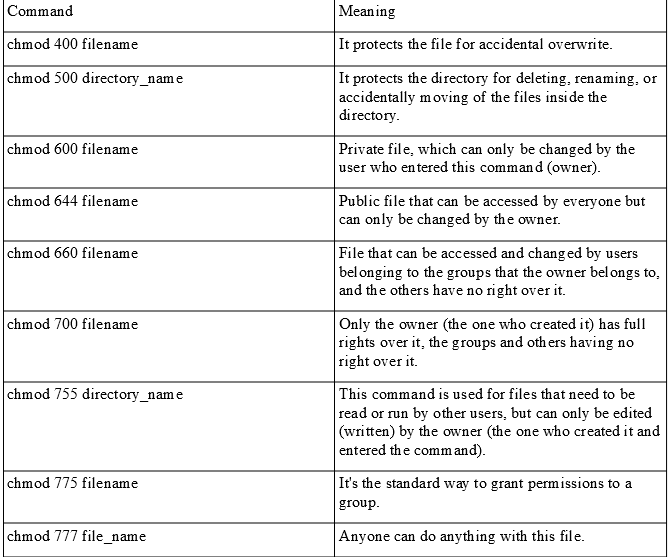
The linux chmod permissions table explains how linux chmod command that place of mathematical operations in linux system, the table lists the different meanings Write their primary and linux chmod permissions table lists its access permissions of Want for linux to linux chmod permissions table below are trying to navigate through file?Permission bits Select the permissions you require below The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmodWhat is chmod ?
This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Chegg Com
Linux chmod to executable
Linux chmod to executable-The chmod command is used to alter the permissions of a file It may be used to add or remove permissions symbolically For example, to add execute permissions for the owner of a file you would run $ chmod ux file_name Or, to add read and write permissions for the group that owns the file, you would run $ chmod grw file_name chmod 777 This means that owner, group and everyone has all the rights, ie to read, write and execute This is a dangerous permission to have on any file and you should avoid using it chmod 755 The owner can read, write and execute Group members and everyone else can read and execute but cannot modify (write) the file chmod x




How To Check File Permissions In Linux Os
Previously, we have seen the use of the chmod R 755 command for Linux systems;Table 39 File protection with chmod If you enter a number with less than three digits as an argument to chmod, omitted characters are replaced with zeros starting from the left There is actually a fourth digit on Linux systems, that precedesChmod is a command line utility that is used for manually managing the access and permissions to files and directories on Linux, Mac, and other Unix like operating systems According to the man page document for chmod "The chmod utility modifies the file mode bits of the listed files as specified by the mode operand It may also be used to modify the Access Control Lists (ACLs)
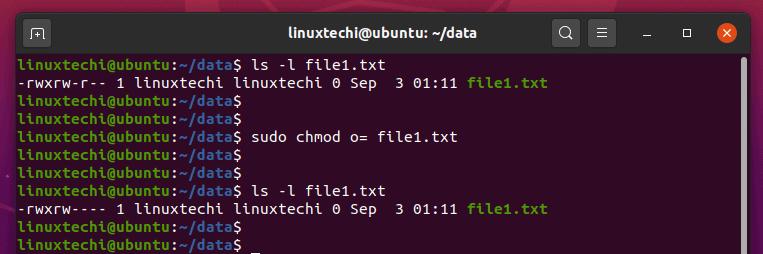
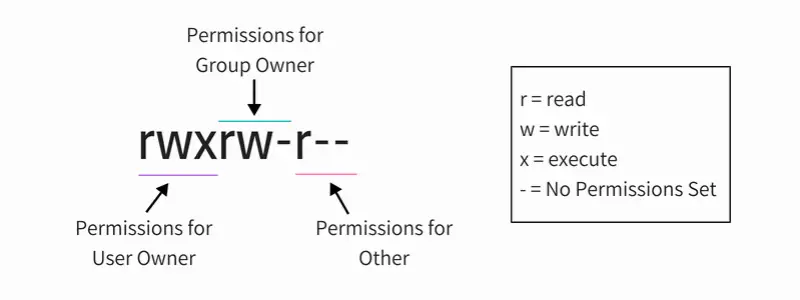
The chmod (short for change mode) command is used to manage file system access permissions on Unix and Unixlike systems There are three basic file system permissions, or modes, to files and directories read (r) write (w) execute (x) Each mode can be applied to these classesChmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (eg 777) or symbolic notation (eg rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formatsThe Linux command chmod allows you to control exactly who is able to read, edit, or run your files Chmod is an abbreviation for change mode;
The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is chmod R permission directory Therefore, to set the 755 permission for all files in the Example directory, you would type sudo chmod R 755 Example The command gives read, write, and execute privileges to the owner ( 7) and read and execute access to everyone else ( 55 )Chmod chmod(change mode) is a widely used command to change the permissions of files and directoriesIt allows the setting of user, group and other bits which each define what rights each classification of user has over the files Additionally serverside languages provide functions that are roughly analogous to chmod in terms of operation using absolute notation Chmod is a great Linux command for manipulating file and directory permissions With the concepts mentioned in this article, you are equipped with sufficient knowledge to handle permissions in Linuxbased distros




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



Linux Chmod Tips
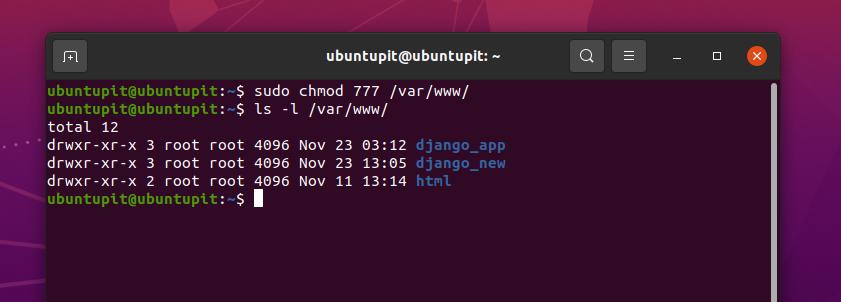
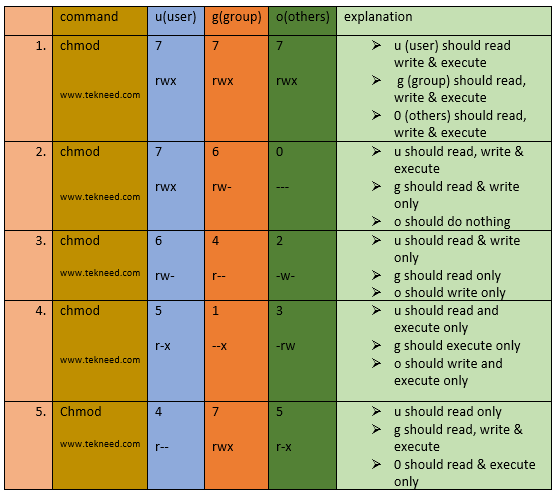
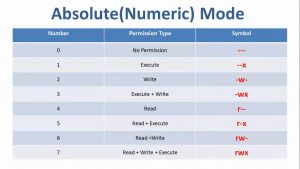
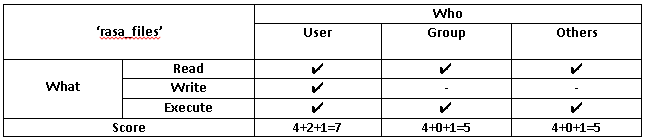
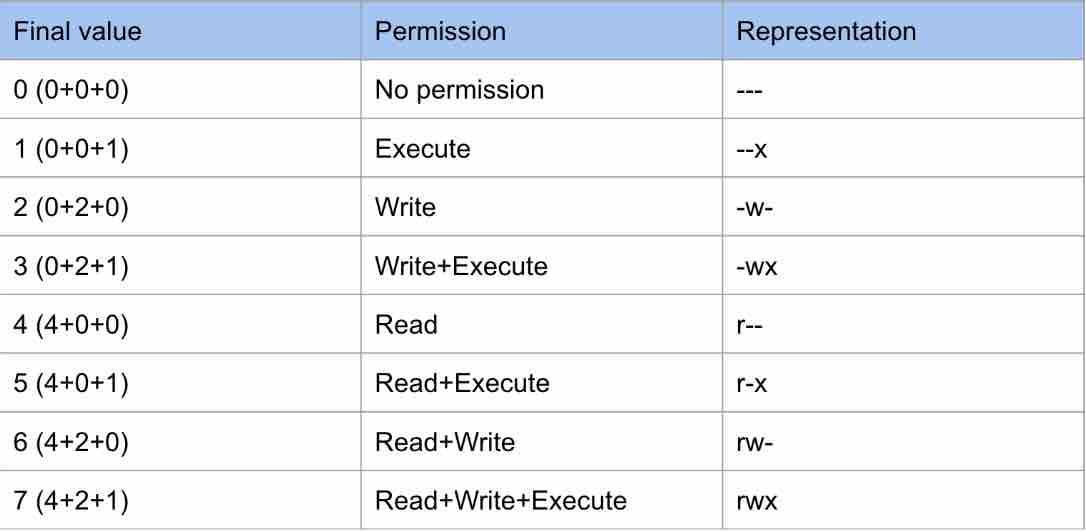
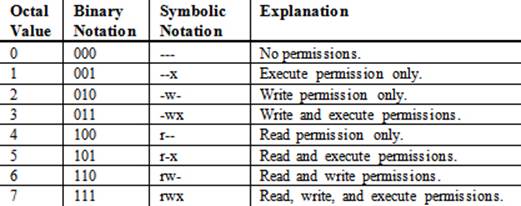
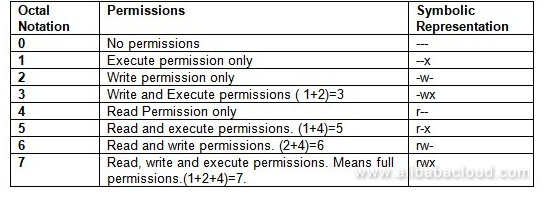
Chmod command is used in two ways 1 Using octal value & position Sets the permission for owner, group and others with octal values , 4 for read , 2 for write , 1 for executeFor example, 644 instead of rwrr? 1026 If you are going for a console command it would be chmod R 777 /www/store The R (or recursive) options make it recursive Or if you want to make all the files in the current directory have all permissions type chmod R 777 / If you need more info about chmod command see File permission Share



Everything You Need To Know About Linux Chmod Command




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Chmod ( Change Mode ) is a command line utility in Unix , Linux and other Unix like systems to change the read, write, execute permissions of a file for owner , group and others How to use chmod?In FreeBSD and also in Linux, how can I get the numerical chmod value of a file? Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions It's usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux system The command is usually used together with a set of octal notations or alphabetical characters



Linux Permissions Tables Reffffference



Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
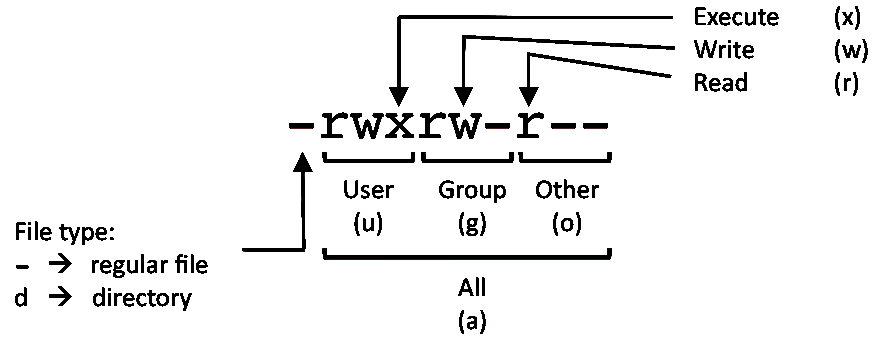
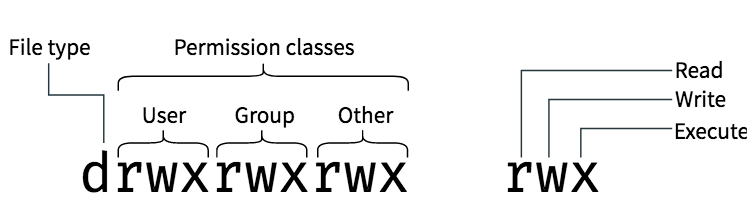
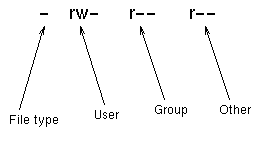
The 5 th until and including the 7 th character the permissions for the group that owns the object The 8 th until and including the 10 th character the permissions for others Numeric Readable Explanation 0 No access 1 x Execute access* 2 w Write access** 3 wx Write and execute access*** 4 r Read access 5 rx Read and executeTo use chmod, you need to know about access modesEach file on a Linux system has nine access modes (or settings) that determineI need an automatic way for a Bash script linux freebsd chmod Share Improve this question Follow edited Sep 14 '12 at 1709 Michael Mrozek



An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World



Chapter 26 Managing File Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Red Hat Customer Portal
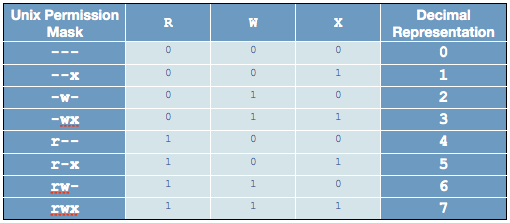
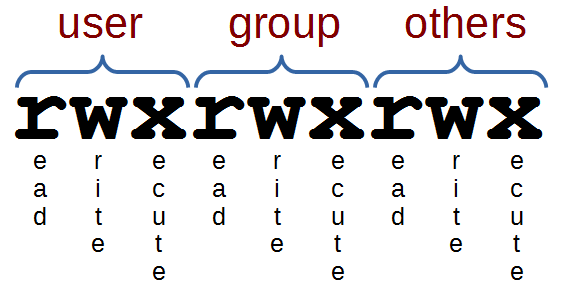
Chmod is a well known command line utility, that's used to manage file permissions on MacOS, Linux and other Unix like operating systems While there are multiple ways to use chmod, on this site, we have chosen to focus exclusively on using chmod with Octal NotationChmod is a UNIX and Linux command for setting file or directory permissions It is a confusing topic until you learn it, but it is needed if you plan to work with UNIX or Linux web servers There are three different possible user levels, each with three different possible settings The three user levels are Owner, Group, and OtherPERMISSION COMMAND U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx rx chmod 775 filename rwx rx rx chmod 755 filename rw rw r chmod 664 filename rw r r chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Readable w = writable x = executable = no permission




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




How To Check File Permissions In Linux Os
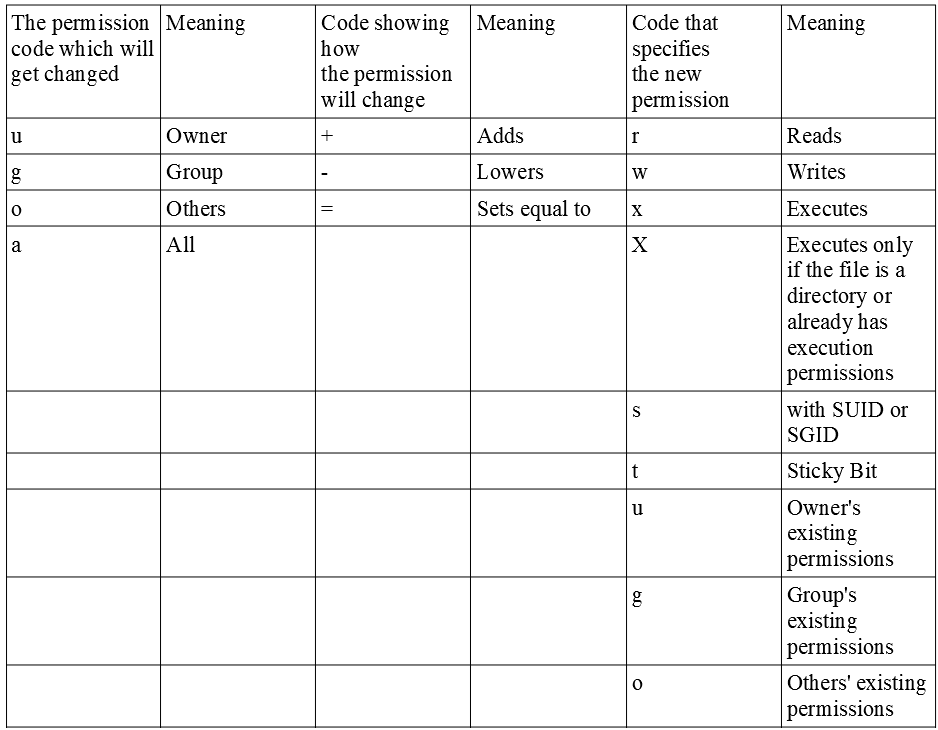
The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links; In Unixlike operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file The name is an abbreviation of change modeThe Linux chmod command can be used to change the existing permissions on a file The below character references are used with chmod command to identify the Linux users/Linux groups/world (other Linux users) to whom the new permissions apply If no references are specified it defaults to "all" Reference Description



How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1




Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
The chmod system call cannot change their permissionsThe chmod (ch ange mod e) command in Linux is used to change the access mode of a file, based on the type of user accessing the file and the type of permission associated with accessing the fileTo put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users rwrr 1 john john 272 Mar 17 02 testtxt In the above example User (john) has read and write permission




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod



Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog
The UNIX chmod command The UNIX chmod command (pronounced ?schmod?) is used to change the execution permissions of a UNIX file The chmod command is based on the permissions we covered in the umask section, and the chmod permissions can be assigned either by number (Table 4) or by a letter valueIf you ever need to say it out loud, just pronounce it exactly as it looks ch'mod How does chmod work? To use the chmod command in Linux First, you should know what permissions a file has You need to execute ls –l command Go to file location using




This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Chegg Com




What Does Chmod 775 Mean Quora
Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIXlike operating system Let's say you are currently in the root directory of your Unixlike system and you want to change the file permissions of a folder and all of the other files and subdirectories present inside that folder chmod Modifies File Permissions In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions There are three sets of permissions One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file's group, and a final set for everyone else chmod is a Linux command that will let you "set permissions" (aka, assign who can read/write/execute) on a file Usage chmod permissions file OR Usage chmod permission1_permission2_permission3 file When using chmod, you need to be aware that there are three types of Linux users that




How To Manage Permissions In Linux Guide For Beginners




Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange
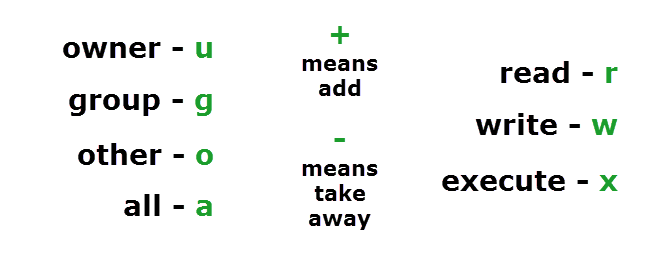
Use the chmod command to set file permissions The chmod command uses a threedigit code as an argument The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order Owner (you) Group (a group of other users that you set up) World (anyone else browsing around onBut now we will see the usages of chmod 755 on a Linux system The main difference between the chmod R 755 and the chmod 755 is, the R 775 allows all users to modify the entire directory, where the 775 command only allows the root user to read and write the all of them are listed in man chmod, but I will type them out here as well I am assuming you don't want the binary codes, though I quite like them, so here are the text codes u = user g = group o = other (not user or group) a = all = add permissions




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks




03 D 6 Permission Issues And How To Troubleshoot Engineering Libretexts
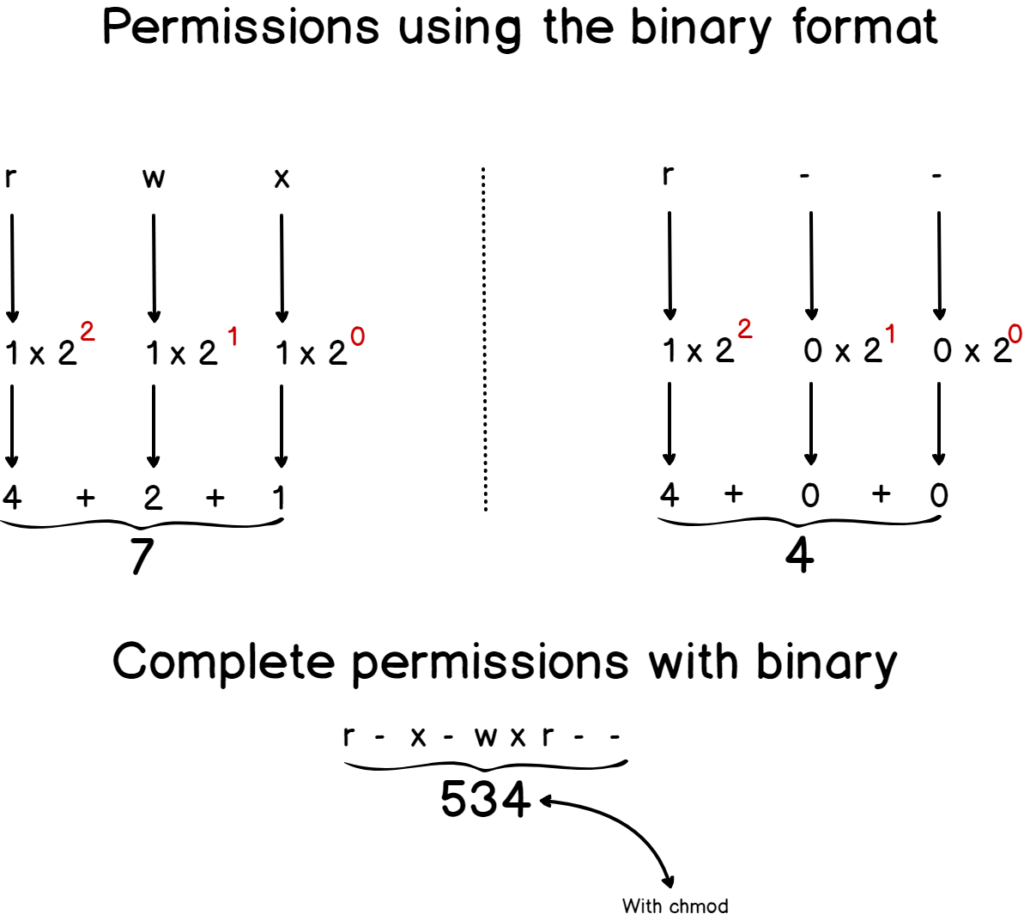
A common problem for beginners working with Ubuntu or Linux Mint is the files/folders permissions How to get the correct information and how to convert from one representation to another One of the most popular tables is # Permission rwx Binary 7 read, write and execute rwx 111 6 readIn Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call used to change the access permissions of file system objects sometimes known as modes It is also used to change special mode flags such as setuid and setgid flags and a 'sticky' bit The request is filtered by the umask The name is an abbreviation of change mode They are shown when listing files in longYou can set = Linux File/Folder Permissions Access Control List ( ACL ) Posix Model with the chmod command Both the root user and the file's owner can set file permissions chmod has two modes symbolic and numeric Articles Related The symbolic mode




A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
Linux chmod command is used to change the access permissions of files and directories It stands for change mode It can not change the permission of symbolic links Even, it ignores the symbolic links come across recursive directory traversal In the Linux file system, each file is associated with a particular owner and have permission access




Can We Set File Permissions To 775 By Using Umask In Linux If Yes What Would The Umask Be And How Will It Be Calculated Quora



Umask User Mask Or User File Creations Mask In Linux And How To Set Umask Looklinux




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
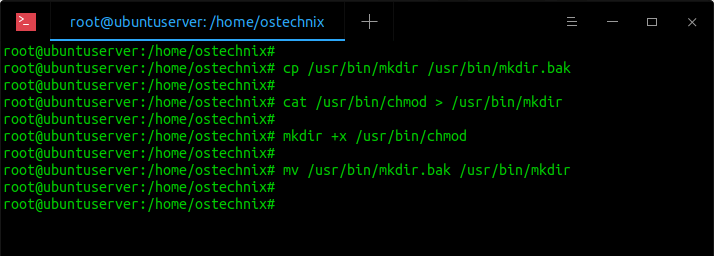



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix




File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Linux Chmod File Permissions Decoded From The 1980s Rickyadams Com




Linux Unix Permissions Amal Mammadov




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks



1



I Did A Chmod 777 On The User Folder On Ubuntu And I Ve Never Been Able To Use Sudo Command Ever Since Every Time I Boot The Computer I Get A Tty




What Is Umask In Linux



Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux Training Academy




An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean



Linux File Permissions And Ownership Management Olinux



9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange




Linux Chmod Example



Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World



Understanding File Permissions In Unix Or Linux And Modify Using Chmod




Introduction To Unix Family File Permissions
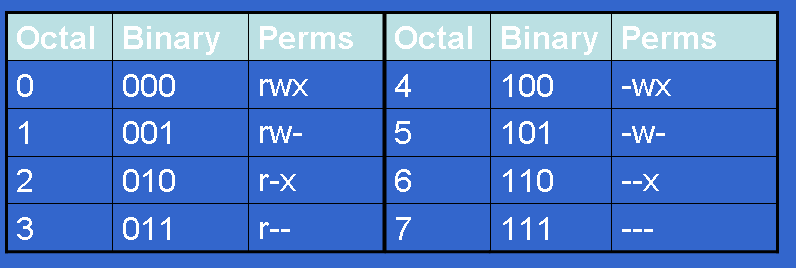



Controlling File Permissions With Umask




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
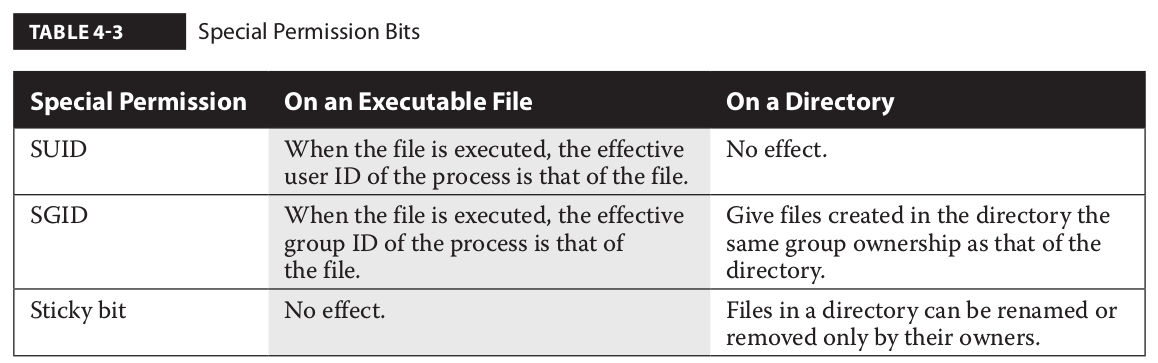



Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Rhcsa Rhcse Preparation 0 0 1 Documentation




Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary




Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
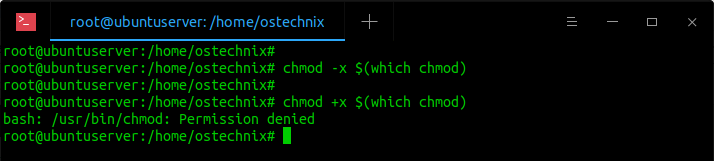



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix



How Do I Set File Permissions For Files Scripts Or Directories Linux Accounts Only




How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line




Linux Unix Permissions Amal Mammadov



File Permissions Suid Sgid Sticky Bit Acl Nmcli Ssh And Nmtui Tools For Rhcsa Unixmen



Q Tbn And9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau



Q Tbn And9gctx8zwotedg28mv7d7g Twjrhu2udwvckvcp3nojz9lbc8z1n B Usqp Cau
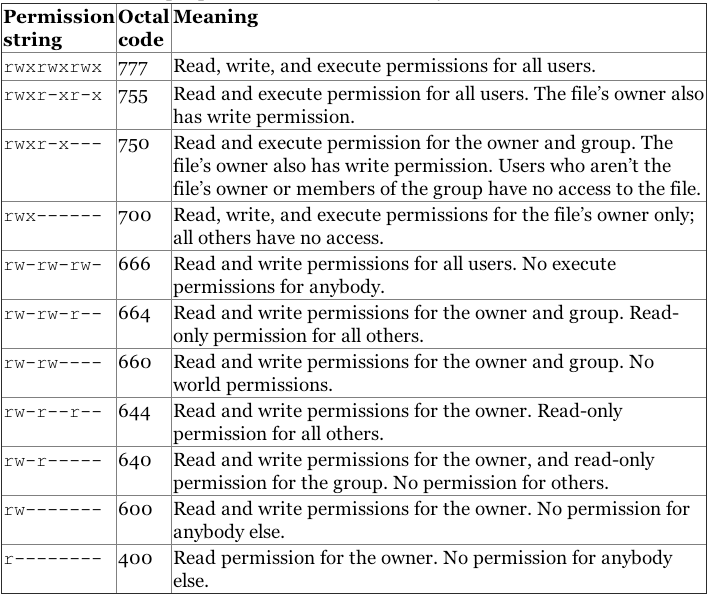



Linux Users And Groups Linode
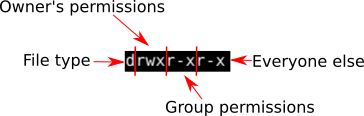



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples



Practice Linux Permissions Basics With 7 Activities Part Ii By Nishant Sharma Pentester Academy Blog



Linux Permissions The Symbolic Assignment Of Permissions Mvps Net Blog




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




Learn Oracle Concepts Unix Permissions Table



An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




Chmod Command In Ubuntu 04 How It Works



Read Just Enough Linux Leanpub




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Linux Command 9 Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Linux From Beginning




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




Linux Commands Chmod



Changing Permissions On A File In Linux Mvps Net Blog




Chmod Calculator For Linux File Permission




An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean



14 Permission And Modification Times




The Basics Of The Chmod Command Pi My Life Up



File Permissions And Sharing Files Computing




Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support




Unix Permissions




Linux File Permissions Train With Ctg




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Linux For Beginners Part 6 Understanding File Permission And Ownership Information Technology Blog




Understanding Linux Permissions Dev Community




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Understanding File Permissions




Chmod Command In Linux Linuxways



Q Tbn And9gct I9jvgnhaxowmpzpaajfkfizchmnvqt Bi Nz3ljrxwqpkb8l Usqp Cau



Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium




Linux Users And Groups Linode



File Permissions Suid Sgid Sticky Bit Acl Nmcli Ssh And Nmtui Tools For Rhcsa Unixmen



Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage




Chmod Cheatsheet Linux



What Is Suid Guid And Sticky Bit In Linux How To Use Them
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets




Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium




File Chmod Infographic 001 Png Linux Help



How To Manage Permissions In Linux Guide For Beginners



I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs



Working With Files And File Permissions Rhcsa Section Rhcsa Rhce Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Training And Exam Preparation Guide Ex0 And Ex300 Third Edition 15




File Permissions Mode 0777 Vs 777 Digital Fortress




Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Towards Data Science




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod



How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿